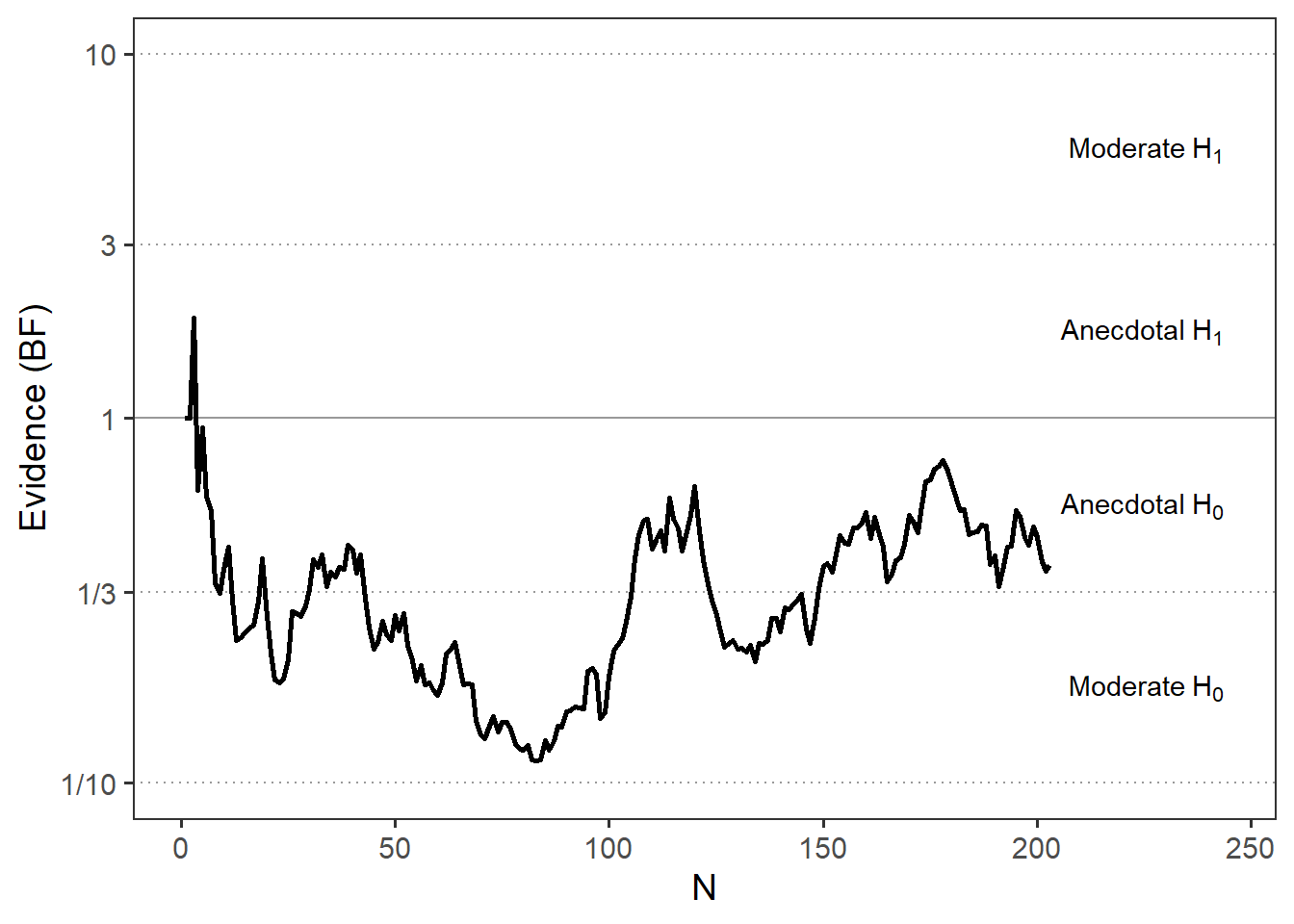| Study | Effect expected | N | Trials | M | SD | Hits (%) | t | p | ES | Var | BF | Direction | Year | Lab/Online |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smokers 3 | ✔ | 203 | 400 | 199.14 | 10.11 | 50.22 | -1.21 | 0.11 | -0.09 | 0 | 0.4 | less | 2017 | 🏠 |
Smokers 3
Hypothesis
In this study, we used cigarette addiction as unconscious drive (see Smokers 1 and Smokers 2). We hypothesized that smoking participants would influence the outcome of a qRNG in such a way that the effect follows a specific pattern derived from post-hoc analyses of the previous studies.
Participants
| Characteristic | Count/Statistic |
|---|---|
| N | 203 |
| Female | 50.25% |
| Male | 49.75% |
| Mean Age | 33.12 years |
| SD Age | 14.44 years |
Materials
All materials and procedural decisions were identical to those of Studies 1 and 2.
Sample Size and Data Analyses
Participants were added until a total of 500 smokers had been reached, including all participants from Studies 1 and 2.
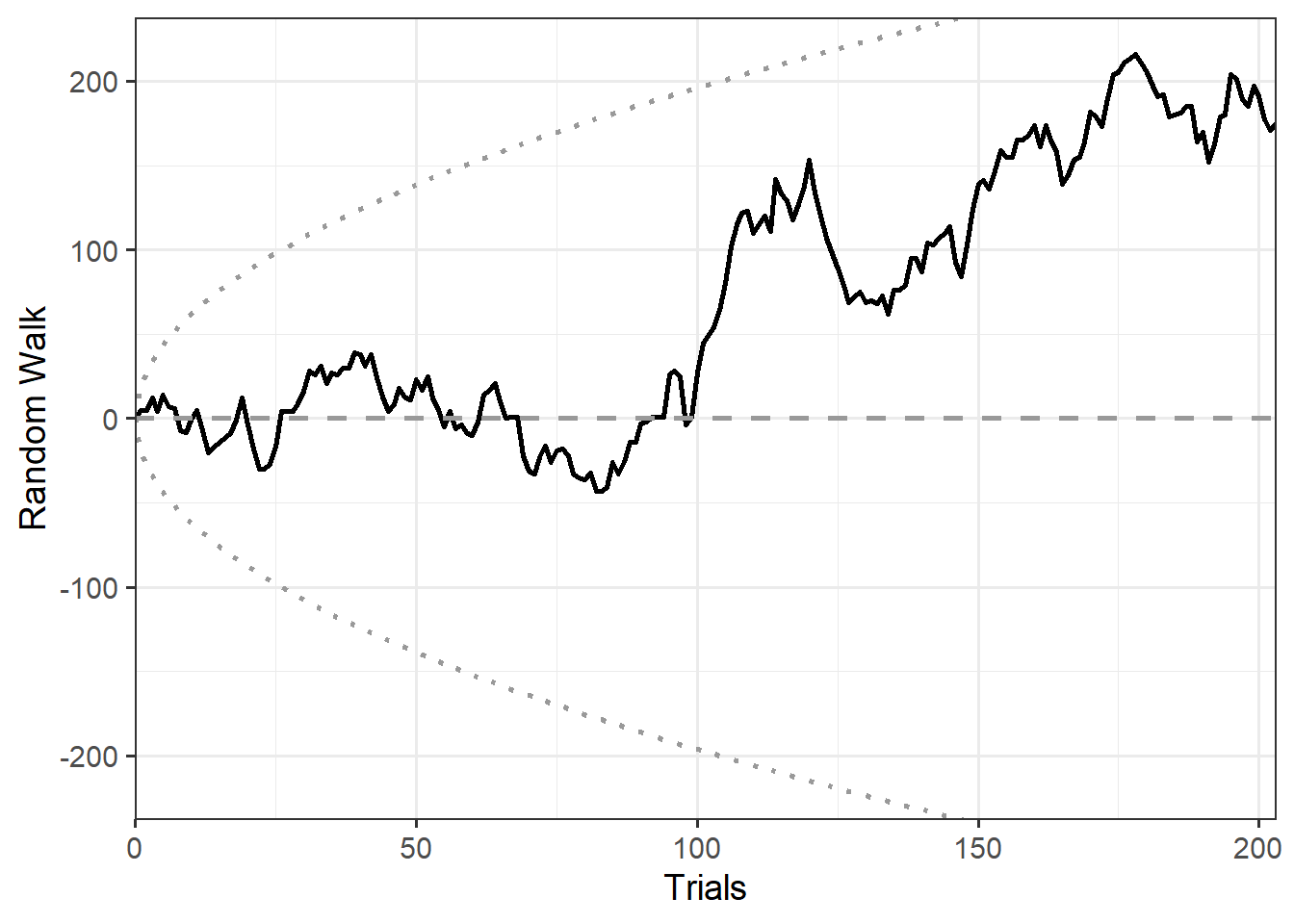
We hypothesized a non-linear effect development resulting in the cumulative z-score of all studies following a fitted dampened harmonic oscillation. To test this hypothesis, we compared the actual cumulative z-score to that of 10,000 simulations and predicted a closer match than 5% of simulations for the following test statistics:
- The area between the experimental data curve and the prediction.
- The Euclidian distance of the local maximum compared with that of the prediction.
- The Euclidian distance of the end point compared with that of the end point of the prediction.
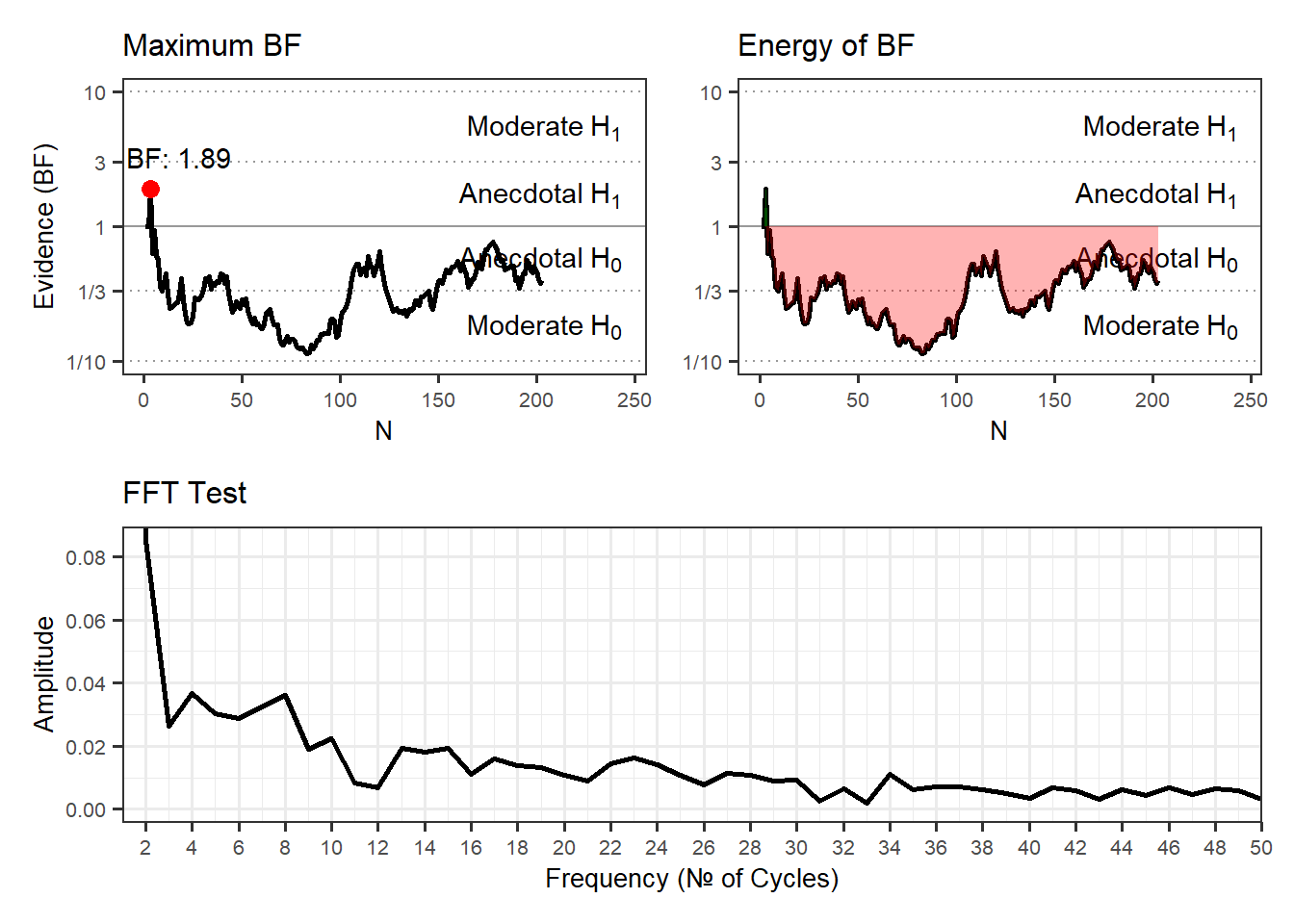
Results of Universal Micro-PK Hypothesis