| Study | Effect expected | N | Trials | M | SD | Hits (%) | t | p | ES | Var | BF | Direction | Year | Lab/Online |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
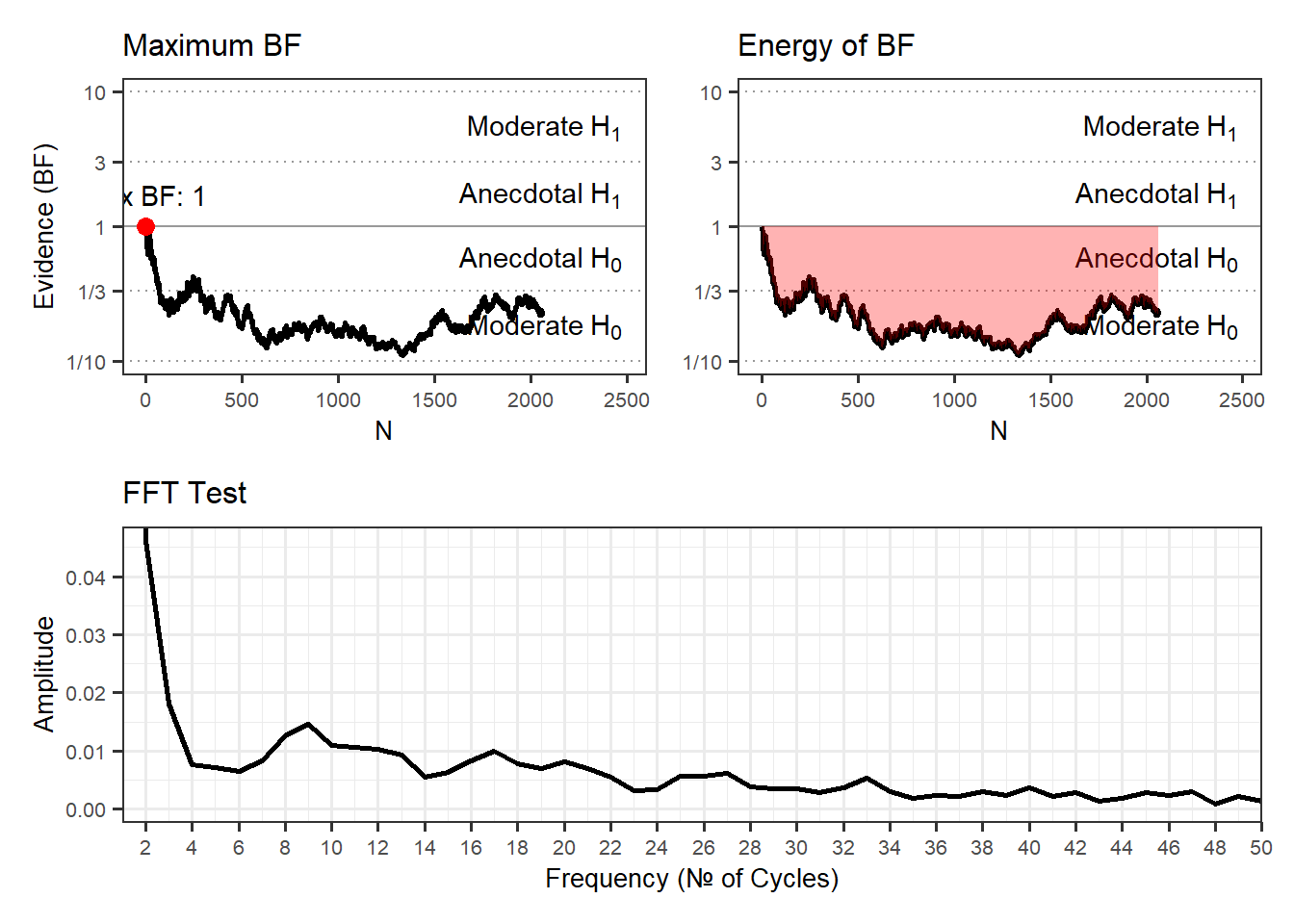
| Priming 2 Exp | ✔ | 2063 | 20 | 9.96 | 2.23 | 49.81 | -0.79 | 0.78 | -0.02 | 0 | 0.09 | greater | 2018 | 🌍 |
| Priming 2 Con | ✖ | 2063 | 20 | 10.02 | 2.23 | 50.08 | 0.32 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.22 | greater | 2018 | 🌍 |
Priming 2
Hypothesis
This study was a direct replication of Priming 1. All predictions were identical to those in the first study.
Participants
| Characteristic | Count/Statistic |
|---|---|
| N | 2063 |
| Female | 42.95% |
| Male | 55.02% |
| Mean Age | 57.37 years |
| SD Age | 15.07 years |
Materials and Procedure
All materials and procedures were identical to those in Priming 1.
Sample Size and Data Analysis
Participant recruitment and data collection for the study were conducted by Norstat, following the same protocol as Study 1. Initially, data collection was planned to stop when the sequential Bayes Factor (BF) reached the predefined threshold, which occurred at n = 937. However, due to concerns about the small predicted effect size and potential lack of statistical power, the researchers decided to continue collecting data. They closely monitored the BF and eventually stopped recruitment when the sample size reached N = 2,063. Demographic data were available for 2,021 participants.
Results of Universal Micro-PK Hypothesis
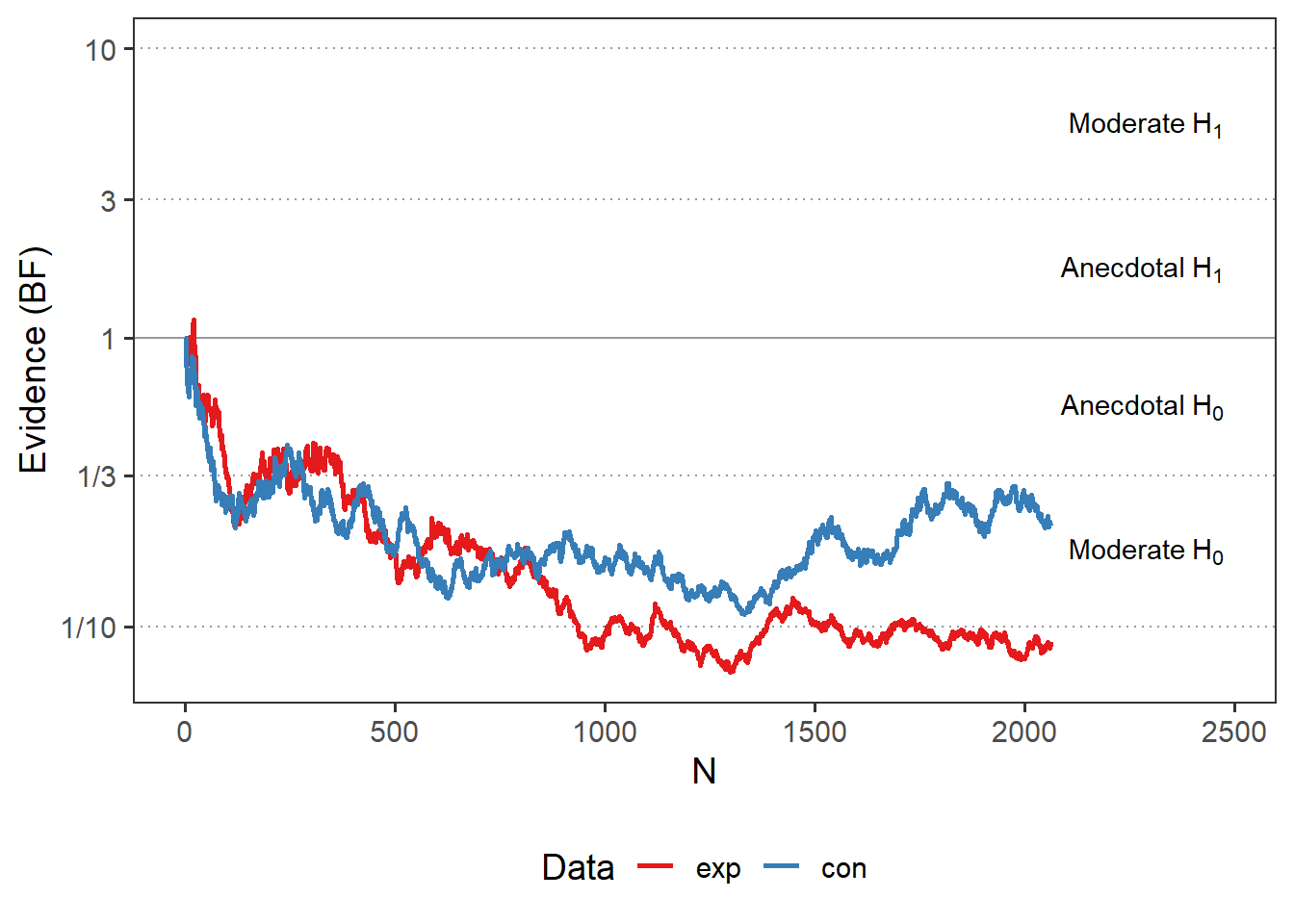
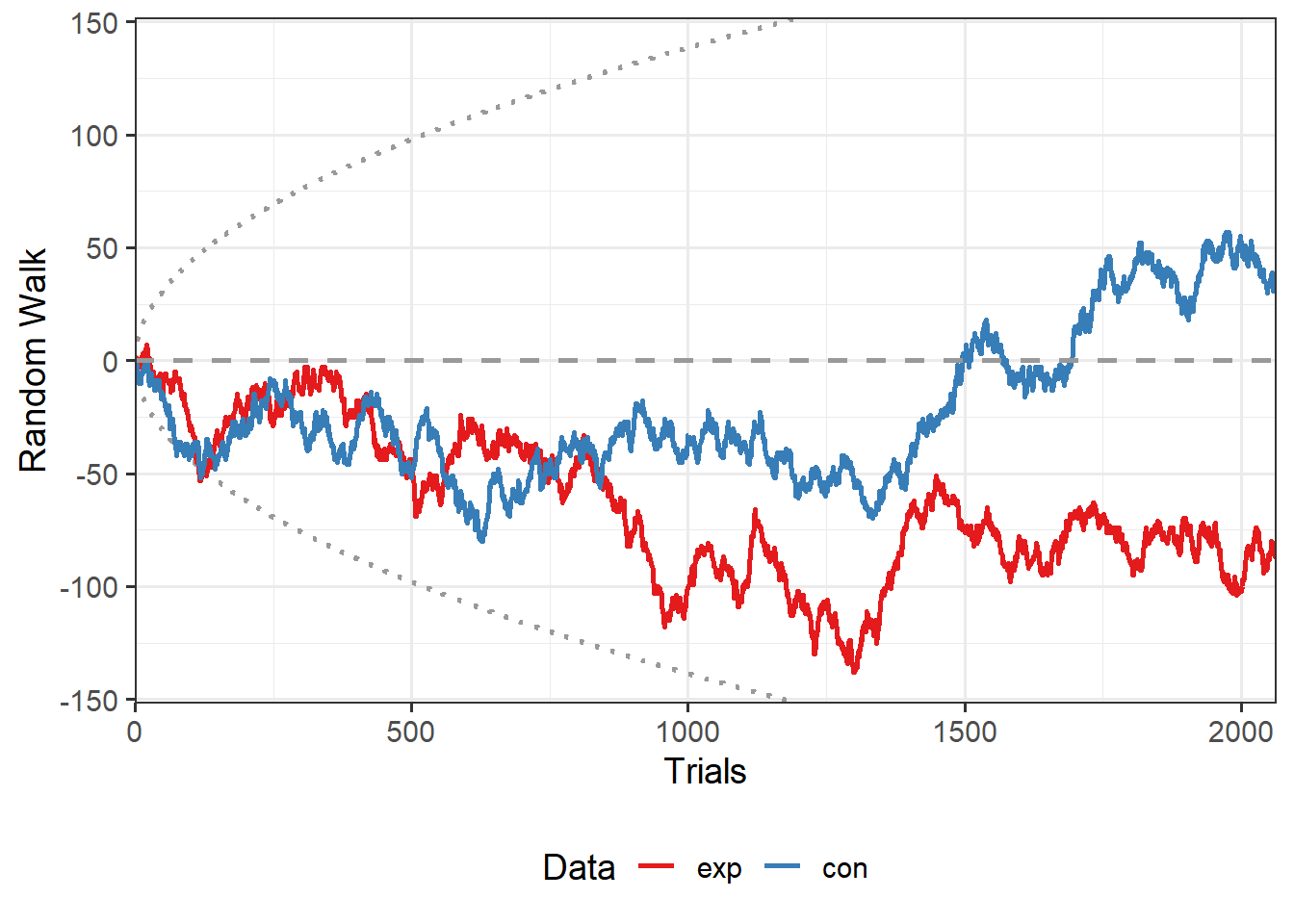
Exp
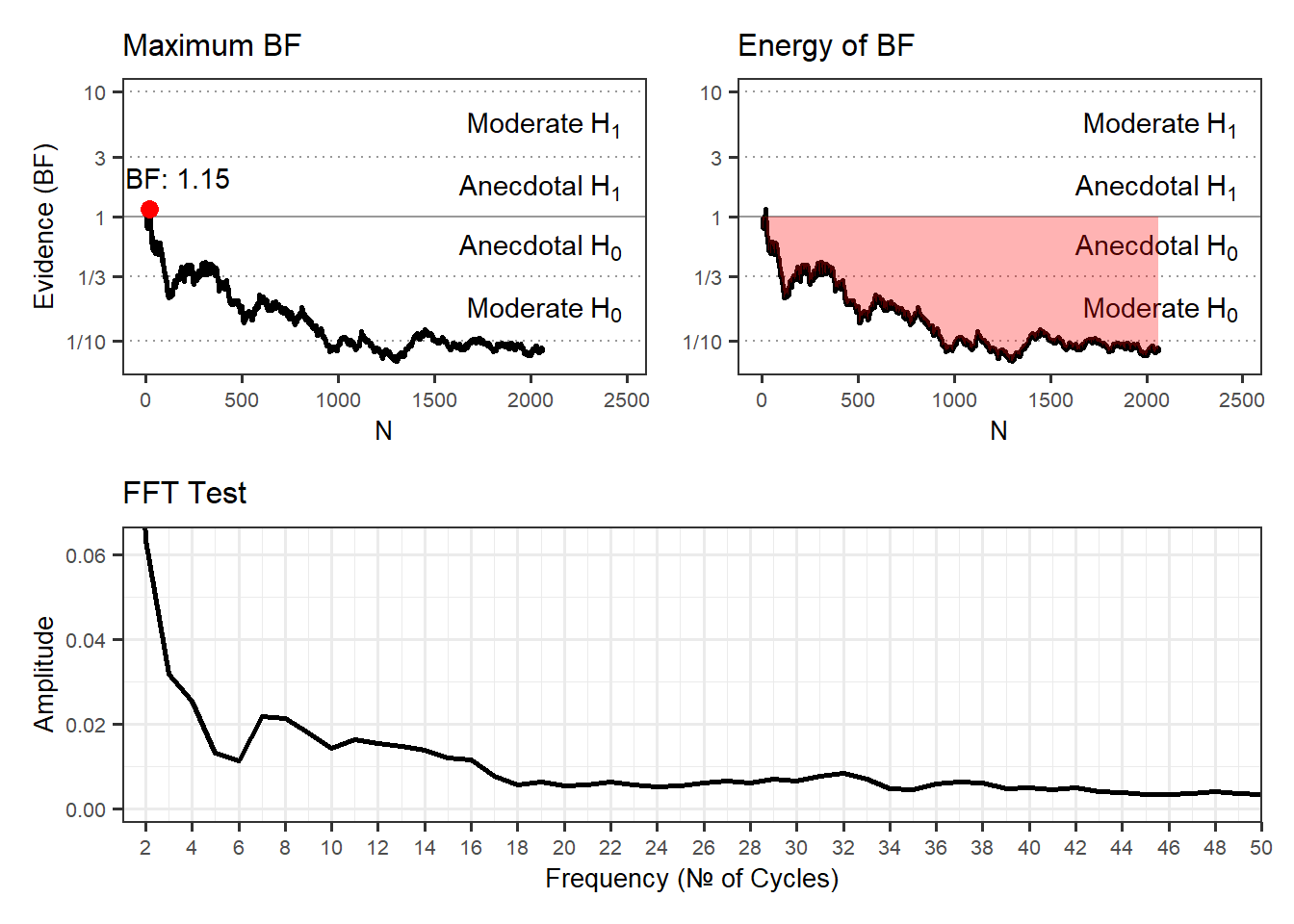
Con